Update 2015-01-02: About a month ago, in early December, 2014,
Google announced that it was working on a new anti-spam API that is intended to replace the traditional CAPTCHA challenge as a method for humans to prove that they are not robots. This is very good news.
This week, I noticed that Akismet is adding a hidden input field to the comment form that contains a timestamp (although the plugin’s PHP puts the initial INPUT element within a P element set to DISPLAY:NONE, when the plugin’s JavaScript updates the value with the current timestamp, the INPUT element jumps outside of that P element). The injected code looks something like this:
<input type=”hidden” id=”ak_js” name=”ak_js” value=”1420256728989″>
I haven’t yet dug into the Akismet code to discover what it’s doing with the timestamp, but I’d be pleased if Akismet is attempting to differentiate humans from bots based on behavior.
Update 2015-01-10: To test the effectiveness of the current version of Akismet, I disabled the anti-spam plugin described in this post on 1/2/2015 and re-enabled it on 1/10/2015. In the span of 8 days, Akismet identified 1,153 spam comments and missed 15 more. These latest numbers continue to support my position that
Akismet is not enough to stop spam comments.
In the endless battle against WordPress comment spam, I’ve developed and then refined a few different methods for preventing spam from getting to the database to begin with. My philosophy has always been that a human visitor and a spam bot behave differently (after all, the bots we’re dealing with are not Nexus-6 model androids here), and an effective spam-prevention method should be able to recognize the differences. I also have a dislike for CAPTCHA methods that require a human visitor to prove, via an intentionally difficult test, that they aren’t a bot. The ideal method, I feel, would be invisible to a human visitor, but still accurately identify comments submitted by bots.
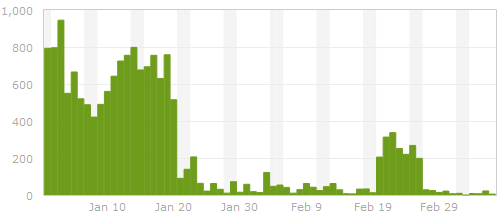
Spam on ardamis.com - before and after
A brief history of spam fighting
The most successful and simple method I found was a server-side system for reducing comment spam by using a handshake method involving timestamps on hidden form fields that I implemented in 2007. The general idea was that a bot would submit a comment more quickly than a human visitor, so if the comment was submitted too soon after the post page was loaded, the comment was rejected. A human caught in this trap would be able to click the Back button on the browser, wait a few seconds, and resubmit. This proved to be very effective on ardamis.com, cutting the number of spam comments intercepted by Akismet per day to nearly zero. For a long time, the only problem was that it required modifying a core WordPress file: wp-comments-post.php. Each time WordPress was updated, the core file was replaced. If I didn’t then go back and make my modifications again, I would lose the spam protection until I made the changes. As it became easier to update WordPress (via a single click in the admin panel) and I updated it more frequently, editing the core file became more of a nuisance.
A huge facepalm
When Google began weighting page load times as part of its ranking algorithm, I implemented the WP Super Cache caching plugin on ardamis.com and configured it to use .htaccess and mod_rewrite to serve cache files. Page load times certainly decreased, but the amount of spam detected by Akismet increased. After a while, I realized that this was because the spam bots were submitting comments from static, cached pages, and the timestamps on those pages, which had been generated server-side with PHP, were already minutes old when the page was requested. The form processing script, which normally rejects comments that are submitted too quickly to be written by a human visitor, happily accepted the timestamps. Even worse, a second function of my anti-spam method also rejected comments that were submitted 10 minutes or more after the page was loaded. Of course, most of the visitors were being served cached pages that were already more than 10 minutes old, so even legitimate comments were being rejected. Using PHP to generate my timestamps obviously was not going to work if I wanted to keep serving cached pages.
JavaScript to the rescue
Generating real-time timestamps on cached pages requires JavaScript. But instead of a reliable server clock setting the timestamp, the time is coming from the visitor’s system, which can’t be trusted to be accurate. Merely changing the comment form to use JavaScript to generate the first timestamp wouldn’t work, because verifying a timestamp generated on the client-side against one generated server-side would be disastrous.
Replacing the PHP-generated timestamps with JavaScript-generated timestamps would require substantial changes to the system.
Traditional client-side form validation using JavaScript happens when the form is submitted. If the validation fails, the form is not submitted, and the visitor typically gets an alert with suggestions on how to make the form acceptable. If the validation passes, the form submission continues without bothering the visitor. To get our two timestamps, we can generate a first timestamp when the page loads and compare it to a second timestamp generated when the form is submitted. If the visitor submits the form too quickly, we can display an alert showing the number of seconds remaining until the form can be successfully submitted. This client-side validation should hopefully be invisible to most visitors who choose to leave comments, but at the very least, far less irritating than a CAPTCHA system.
It took me two tries to get it right, but I’m going to discuss the less successful method first to point out its flaws.
Method One (not good enough)
Here’s how the original system flowed.
- Generate a first JS timestamp when the page is loaded.
- Generate a second JS timestamp when the form is submitted.
- Before the form contents are sent to the server, compare the two timestamps, and if enough time has passed, write a pre-determined passcode to a hidden INPUT element, then submit the form.
- After the form contents are sent to the server, use server-side logic to verify that the passcode is present and valid.
The problem was that it seemed that certain bots could parse JavaScript enough to drop the pre-determined passcode into the hidden form field before submitting the form, circumventing the timestamps completely and defeating the system.
Because the timestamps were only compared on the client-side, it also failed to adhere to one of the basic tenants of form validation – that the input must be checked on both the client-side and the server-side.
Method Two (better)
Rather than having the server-side validation be merely a check to confirm that the passcode is present, method two compares the timestamps a second time on the server side. Instead of a single hidden input, we now have two – one for each timestamp. This is intended to prevent a bot from figuring out the ultimate validation mechanism by simply parsing the JavaScript. Finally, the hidden fields are not in the HTML of the page when it’s sent to the browser, but are added to the form via jQuery, which makes it easier to implement and may act as another layer of obfuscation.
- Generate a first JS timestamp when the page is loaded and write it to a hidden form field.
- Generate a second JS timestamp when the form is submitted and write it to a hidden form field.
- Before the form contents are sent to the server, compare the two timestamps, and if enough time has passed, submit the form (client-side validation).
- On the form processing page, use server-side logic to compare the timestamps a second time (server-side validation).
This timestamp handshake works more like it did in the proven-effective server-side-only method. We still have to pass something from the comment form to the processing script, but it’s not too obvious from the HTML what is being done with it. Furthermore, even if a bot suspects that the timestamps are being compared, there is no telling from the HTML what the threshold is for distinguishing a valid comment from one that is invalid. (The JavaScript could be parsed by a bot, but the server-side check cannot be, making it possible to require a slightly longer amount of time to elapse in order to pass the server-side check.)
The same downside plagued me
For a long time, far longer than I care to admit, I stubbornly continued to modify the core file wp-comments-post.php to provide the server-side processing. But creating the timestamps and parsing them with a plug-in turned out to be a simple matter of two functions, and in June of 2013 I finally got around to doing it the right way.
The code
The plugin, in all its simplicity, is only 100 lines. Just copy this code into a text editor, save it as a .php file (the name isn’t important) and upload it to the /wp-content/plugins directory and activate it. Feel free to edit it however you like to suit your needs.
<?php
/*
Plugin Name: Timestamp Comment Filter
Plugin URI: //ardamis.com/2011/08/27/a-cache-proof-method-for-reducing-comment-spam/
Description: This plugin measures the amount of time between when the post page loads and the comment is submitted, then rejects any comment that was submitted faster than a human probably would or could.
Version: 0.1
Author: Oliver Baty
Author URI: //ardamis.com
Copyright 2013 Oliver Baty (email : obbaty@gmail.com)
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
*/
// http://wordpress.stackexchange.com/questions/6723/how-to-add-a-policy-text-just-before-the-comments
function ard_add_javascript(){
?>
<script type="text/javascript" src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function(){
ardGenTS1();
});
function ardGenTS1() {
// prepare the form
$('#commentform').append('<input type="hidden" name="ardTS1" id="ardTS1" value="1" />');
$('#commentform').append('<input type="hidden" name="ardTS2" id="ardTS2" value="1" />');
$('#commentform').attr('onsubmit', 'return validate()');
// set a first timestamp when the page loads
var ardTS1 = (new Date).getTime();
document.getElementById("ardTS1").value = ardTS1;
}
function validate() {
// read the first timestamp
var ardTS1 = document.getElementById("ardTS1").value;
// alert ('ardTS1: ' + ardTS1);
// generate the second timestamp
var ardTS2 = (new Date).getTime();
document.getElementById("ardTS2").value = ardTS2;
// alert ('ardTS2: ' + document.getElementById("ardTS2").value);
// find the difference
var diff = ardTS2 - ardTS1;
var elapsed = Math.round(diff / 1000);
var remaining = 10 - elapsed;
// alert ('diff: ' + diff + '\n\n elapsed:' + elapsed);
// check whether enough time has elapsed
if (diff > 10000) {
// submit the form
return true;
}else{
// display an alert if the form is submitted within 10 seconds
alert("This site is protected by an anti-spam feature that requires 10 seconds to have elapsed between the page load and the form submission. \n\n Please close this alert window. The form may be resubmitted successfully in " + remaining + " seconds.");
// prevent the form from being submitted
return false;
}
}
</script>
<?php
}
add_action('comment_form_before','ard_add_javascript');
// http://wordpress.stackexchange.com/questions/89236/disable-wordpress-comments-api
function ard_parse_timestamps(){
// Set up the elapsed time, in miliseconds, that is the threshold for determining whether a comment was submitted by a human
$intThreshold = 10000;
// Set up a message to be displayed if the comment is blocked
$strMessage = '<strong>ERROR</strong>: this site uses JavaScript validation to reduce comment spam by rejecting comments that appear to be submitted by an automated method. Either your browser has JavaScript disabled or the comment appeared to be submitted by a bot.';
$ardTS1 = ( isset($_POST['ardTS1']) ) ? trim($_POST['ardTS1']) : 1;
$ardTS2 = ( isset($_POST['ardTS2']) ) ? trim($_POST['ardTS2']) : 2;
$ardTS = $ardTS2 - $ardTS1;
if ( $ardTS < $intThreshold ) {
// If the difference of the timestamps is not more than 10 seconds, exit
wp_die( __($strMessage) );
}
}
add_action('pre_comment_on_post', 'ard_parse_timestamps');
?>
That’s it. Not so bad, right?
Final thoughts
The screen-shot at the beginning of the post shows the number of spam comments submitted to ardamis.com and detected by Akismet each day from the end of January, 2012, to the beginning of March, 2012. The dramatic drop-off around Jan 20 was when I implemented the method described in this post. The flare-up around Feb 20 was when I updated WordPress and forgot to replace the modified core file for about a week, illustrating one of the hazards of changing core files.
If you would rather not add any hidden form fields to the comment form, you could consider appending the two timestamps to the end of the comment_post_ID field. Because its contents are cast as an integer in wp-comments-post.php when value of the $comment_post_ID variable is set, WordPress won’t be bothered by the extra data at the end of the field, so long as the post ID comes first and is followed by a space. You could then just explode the contents of the comment_post_ID field on the space character, then compare the last two elements of the array.
If you don’t object to meddling with a core file in order to obtain a little extra protection, you can rename the wp-comments-post.php file and change the path in the comment form’s action attribute. I’ve posted logs showing that some bots just try to post spam directly to the wp-comments-post.php file, so renaming that file is an easy way to cut down on spam. Just remember to come back and delete the wp-comments-post.php file each time you update WordPress.